Principle of Flame Detection:Insight into the Optical Characteristics and Detection Techniques of Flames
Flame detection is a crucial aspect of fire prevention and safety systems, relying on the unique physical and optical characteristics of flames. During combustion, whether it is solid, liquid, or gaseous fuel, heat and accompanying light radiation are released, forming the basis of flame detection.
How can flames be detected?
Burning flames possess various characteristics that can be utilized to detect their presence or absence, such as heat intensity, ionization state, radiation from different parts of the flame, spectra, flame flickering or pulsation, pressure differentials, and sound.
All fuel combustion processes emit a certain amount of ultraviolet radiation and significant amounts of infrared radiation. The spectrum ranges from infrared to visible light and ultraviolet. Therefore, the entire spectrum can be utilized to detect the presence or absence of flames.
Flames also have different types?
In general, coal powder flames contain non-luminous gases such as CO2 and water vapor, as well as hot glowing particles and carbon particles, which emit strong infrared, visible light, and some ultraviolet radiation. However, ultraviolet radiation is easily absorbed and weakened by combustion products and ash particles. Therefore, visible light or infrared flame detectors are suitable for detecting coal powder combustion flames.
For oil flames used in furnaces and ignition, in addition to CO2 and water vapor, there are a large number of luminescent carbon black particles, which also emit strong visible light, infrared, and ultraviolet radiation. Therefore, detection elements sensitive to these three types of flames can be used for measurement.
When combustible gases are burned as the main fuel, the initial combustion zone of the flame emits strong ultraviolet radiation. In this case, ultraviolet flame detectors can be used for detection.
Principle of Flame Detection
Principles of Flame Detection involve utilizing various characteristics exhibited by burning flames to determine their presence or absence. These characteristics include heat intensity, ionization state, radiation emitted from different parts of the flame, spectra, flame flickering or pulsation, pressure differentials, and sound.
Flames emit electromagnetic radiation across a broad spectrum, including infrared (IR), visible light, and ultraviolet (UV) wavelengths, depending on the fuel source. Optical technologies are commonly employed in flame detectors to capture and analyze this radiation. Optical flame-sensing technologies have been developed utilizing UV, UV/IR, and multi-spectrum infrared to detect flames originating from different fuel sources. These flame detection systems rely on line-of-sight detection of the radiation emitted in specific spectral bands to determine the presence or absence of a flame.
Additionally, all combustion processes produce ultraviolet radiation and significant amounts of infrared radiation. The emitted spectrum spans from infrared to visible light and ultraviolet. Therefore, the entire spectrum can be leveraged for flame detection, utilizing appropriate sensors and detectors to capture and interpret the radiation signals, thus enabling reliable flame detection.

Applications and Recommendations for Flame Sensors
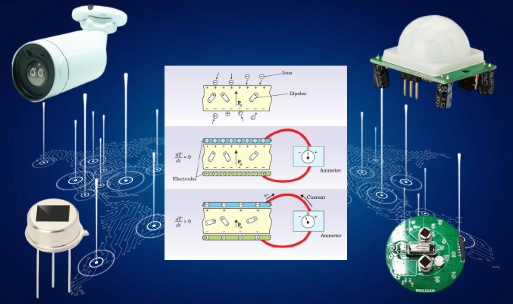
Pyroelectric Flame Sensor: Operating based on the thermoelectric effect, the Pyroelectric flame sensor converts the temperature changes generated when the sensing element detects the infrared signals emitted by flames into voltage signals to determine the presence of flames.
Photoconductive Flame Sensor: Operating based on the photoconductive effect, the photoconductive flame sensor converts the changes in conductivity generated when the sensing element detects the infrared signals emitted by flames into voltage signals to determine the presence of flames.
Ultraviolet Flame Sensor: Ultraviolet flame sensors utilize the radiation characteristics of flames in the ultraviolet spectrum for detection.
We highly recommend the Pyroelectric Flame Sensor
Pyroelectric Flame Sensor
Fire water cannons, also known as fire monitors or fire monitors, are automated firefighting facilities designed to discharge water or firefighting agents to extinguish fires. They are commonly found in large open spaces such as factories, warehouses, industrial buildings, shopping malls, sports stadiums, and logistics parks. Fire water cannons are considered intelligent systems as they incorporate tracking and positioning capabilities to deliver targeted firefighting jets.
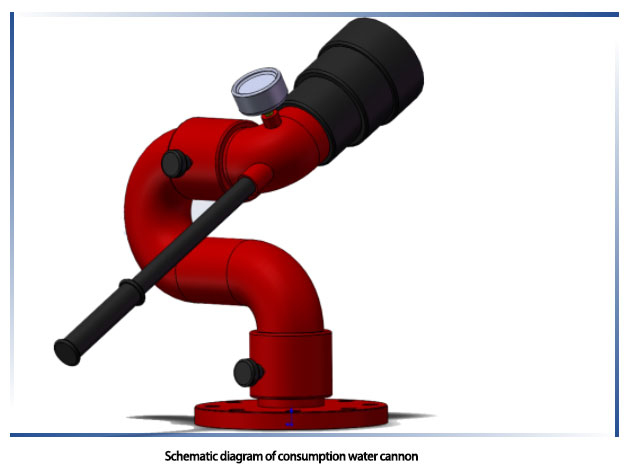
A fire water cannon consists of several components, each serving a different function, working together to enhance the functionality of the firefighting system. These components typically include: Outer Shell, Turret, Sensor Devices, Central Processor, Power Supply, Motor, Camera, Decoder, and Flange.
Winsen Pyroelectric Flame Sensors and Modules

The RPFA913CC series of Pyroelectric flame sensors utilize lithium tantalate (LiTaO3) single crystal as the sensitive material. Lithium tantalate has a Curie temperature above 600°C, low relative dielectric constant, and high detectivity. The Pyroelectric coefficient of the material shows minimal variations with temperature within a wide range of room temperatures. The temperature stability of the sensor's performance is excellent, and it exhibits consistent spectral response within the wavelength range of 1 to 20 μm.
| Part No. | RPFA913CC | RPFA913CD | RPFA913CE | RPFA913CF | RPFA913CG |
| Center wavelength (nm) | 3800±40 | 4300±50 | 4400±40 | 4480±40 | 5000±40 |
| Full width at half maximum FWHM (nm) | 180±20 | 600±40 | 400±20 | 620±20 | 180±20 |
| Transmittance (%) | >90% | >90% | >90% | >85% | >90% |
The RPFA913CC series of Pyroelectric flame sensors offer the following features and are widely applied in various settings:
- 1.High Sensitivity and Long-Distance Detection: These sensors are highly sensitive and capable of detecting flames from long distances. They can effectively detect flames even at a significant range, enabling early fire detection and prevention.
- 2.Wide Field of View and Broad Detection Range: The sensors have a large field of view, allowing them to cover a wide area for flame detection. They are suitable for applications where a broad detection range is required, such as oil storage depots, large warehouses, factory workshops, forests, and charging stations.
- 3.Low Noise and Strong Anti-Vibration Interference: The sensors have low noise levels and are resistant to vibration interference. This ensures accurate and reliable flame detection even in environments with vibrations or other disturbances.
The RPFA913CC series of Pyroelectric flame sensors provide enhanced fire safety measures by offering reliable flame detection capabilities in various applications and environments. They can also be integrated with ultraviolet flame sensor for customized module solutions.
These flame sensors are widely used as standard equipment in high-risk areas prone to fires, such as petroleum and chemical industries, paper manufacturing, forested areas, and garages. They are also increasingly being adopted in high-end residential, commercial, and general industrial sectors.